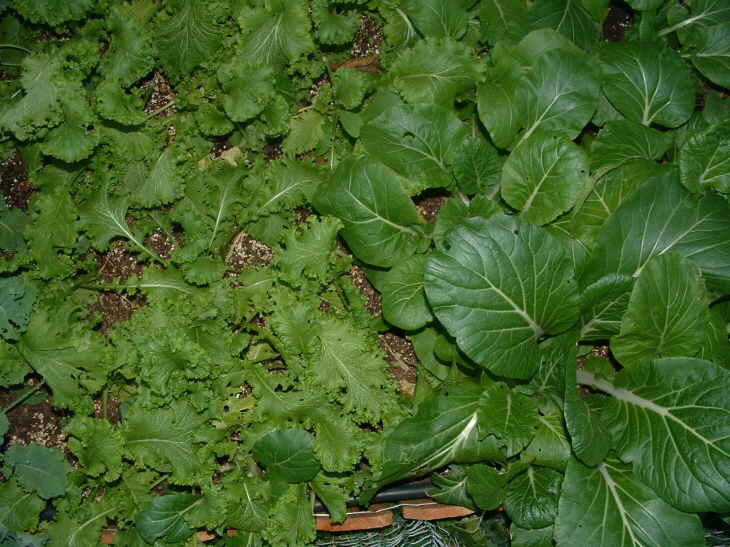
Mustard greens 갓
페이지 정보
작성자뽕킴 댓글 0건 조회 3,809회 작성일 10-03-01 23:00본문
갓(Brassica juncea Czern et Cosson var. integrifolia Sinskaja)은 십자화과의 한해 또는 두해살이풀이다.
십자화과(겨자과=평지과=배추과) 배추속에 속하는 식물은 전세계에 약 40종이 있으며 주로 지중해 부근에 분포한다. 보통 1년초 또는 겨울을 넘기는 월년초 또는 2년초로서 뿌리는 기둥 모양이다. 우리나라에 자라고 있는 배추속 식물은 유채, 배추, 겨자, 갓, 양배추 등이 있다.
갓의 키는 1m 가량 자라고 근생엽은 넓은 타원형과 도란형이며 길이 60~80cm이다. 꽃이 노랗게 십자모양으로 총생화서이다. 열매는 각과이며 꼬투리는 원기둥 모양이며 씨는 갈색은 띤 노란색이다. 흔히 밭에서 재배하며 들로 퍼져나가 논두렁이나 밭둑 개울가에 저절로 자라기도 한다.
갓의 다른 이름은 개, 대개, 추엽개, 황개 라고도 부른다. 개화기는 4~6월이고 결실기는 5~8월이다. 갓의 어린 줄기와 잎, 종자도 약으로 사용한다.
갓은 맛이 맵고 달며 성질은 따뜻하며 독이 없다. 폐와 위에 들어가며 겸하여 신에도 들어간다. 소통폐, 거담, 온중, 이기하는 효능이 있다. 일찍이 중국에서는 기원전 12세기 주(周)나라 때 갓의 종자를 향신료로 사용하였다고 기록은 알려준다.
강한 매운맛을 내는 <겨자>는 갓의 종자의 분말을 이용하는데, 토종겨자와 서양겨자(머스타드)가 있으며, 겨자라고 할 때 일반적으로 전자를 가리킨다. 매운맛의 기본이 되는 성분은 동일하지만 양자의 차이는 원료로 이용되는 식물의 차이가 있다.
토종겨자는 본래는 떫은 맛을 제거해서 이용하였는데 현재에는 서양겨자와 마찬가지로 미지근한 물로 녹여서 이용되고 있다. 어묵이나 고기요리, 생선회(특히 해파리 회) 등의 소스등의 양념으로 귀한 대접을 받고 있다. 서양겨자는 향기도 매운 맛도 부드러운 화이트 머스타드와 맵고 맛이 강한 블랙 머스타드가 있으며 종자를 그대로 또는 분말로 해서 이용하기도 한다.
겨자채의 종류에는 크게 잎겨자채류, 고채류, 다육성 고채류, 줄기고채류, 뿌리고채류라는 그룹으로 나누는데 모두 톡 쏘는 매운맛과 향기가 있고 비타민 A와 C가 풍부한 것이 특징이다. 일본에서는 잎겨자채와 후꾸오까의 산호채가 인기가 있는데 포기는 작지만 강한 매운맛과 선명한 엽색이 특징으로 봄에 유채와 비슷한 황색의 꽃을 피우며 고채류에는 녹색잎의 청엽고채와 잎이 자홍색을 하고 있는 적고채가 있고, 중앙의 엽맥이 넓고 잎이 두꺼운 것이 특징인 다육성 고채에는 삼지고채, 유하고채가 대표 품종이며 그밖에 황겨자채, 대엽고채, 머스터드그린, 가쓰오채가 재배되고 있다.
중국의 고의서 <명의별록>에 의하면 갓은 "신의 사기를 제거하고 구규를 이롭게 하고 눈과 귀를 밝게 하며 안중한다. 오래 먹으면 중초를 따뜻하게 한다. 또한 <식료본초>에서도 "해역을 치료하고 하기, 눈을 밝게하며 두면풍을 치료한다." 중국의 <본초강목>에서도 "폐를 통하게 하며 가래를 삭이고 가슴을 이롭게하며 식욕을 돋운다." 라고 기록하고 있다.
복용 방법은 갓을 달인 물이나 찧은 즙을 복용한다. 외용시는 약성이 남게 태운 다음 갈아서 가루내어 뿌리거나 달인 물로 씻는다. 주의해야 할 점은 종기, 눈병, 치질, 변혈 및 평소 열이 성한 자는 먹어서는 안된다.
잇몸이 진물러 썩은 냄새가 나는 물이 나올 때는 갓의 줄기를 약성이 남게 태운 다음 갈아서 가루내어 여러번 바른다. 옻이 올라 생긴 피부병으로 가려울 때는 갓의 전초를 달인 물로 씻는다. 치질로 붓고 아플 때는 갓의 잎을 찧어 떡처럼 만들어 자주 아픈 곳에 댄다.
갓의 종류도 많아 청개, 자개, 백개, 황개 등이 있다. 갓의 씨앗은 한담으로 인한 해수천식과 흉협통에 쓰고 담체를 소통시켜 경락과 관절의 마비 동통을 풀어 준다. 종기에는 짓찧어 붙인다.
일본에서 펴낸 <건강, 영양 식품사전>에서는 갓에 대해서 다음과 같이 기록하고 있다.
[갓
독특한 매운맛이 식욕을 증진시킨다.
유채와 구로가라시의 자연교배잡종(自然交配雜種)으로 유채과(油菜科)에 속하는 1년초이다. 엽개자채류(葉芥子菜類), 고채류(高菜類), 줄기고채류, 뿌리개자채류 등 종류가 다양하다.
이중에 잎을 식용으로 하는 것은 잎 갓과 고채류로 절여서 먹는 경우가 많다. 줄기고채의 비대(肥大)한 줄기를 절인 것이 중국 요리에서 사용되는 착채(搾菜:짠나물)이다.
잎을 이용한 갓이나 고채에는 잎갓, 황갓, 산조채(山潮菜), 대엽(大葉)고채, 가쯔오채등이 있는데, 모두 특유의 매운맛이 있다. 이 매운 성분은 시니그린이라는 배당체(配糖體)이다. 영양 성분으로서는 카로틴, 비타민 C, 철분을 많이 함유하고 있다.
갓, 고채를 절인 것은 볶음밥이나, 라면에 넣어도 맛이 좋다. 톡쏘는 매운맛이 식욕(食慾)을 돋구며, 더운 여름철 일품(一品)으로 최적이다.]
북한에서는 겨자, 갓, 백겨자, 흑겨자의 종류를 모두 개자라고 하며 약용하거나 찜질용으로 사용하는데 <동의학사전>에서는 개자에 관해서 이렇게 기록하고 있다.
[개자(芥子) // 겨자, 계자 // [본초]
배추과에 속하는 이년생 풀인 겨자(Brassica cernua Forb. et Hemsl.), 갓(Brassica Juncea Coss.), 백겨자(Brassica alba (L.) Boiss.), 흑겨자(Brassica nigra Koch)의 여문 씨를 말린 것이다.
겨자, 갓(황개자), 흑개자, 백개자는 각지에서 심는다. 꼬투리가 누렇게 될 때 줄기채로 베어 말린 다음 씨를 털어 모은다. 맛은 맵고 성질은 따뜻하다. 폐경(肺經)에 작용한다. 폐를 덥혀주고 담(痰)을 삭이며 기침을 멈추고 부종을 내리며 통증을 멈춘다. 또한 자극작용이 있으므로 소량을 먹어도 소화액이 잘 분비되고 위장관의 운동이 세진다. 그러나 많은 양을 먹으면 토하거나 위염이 생길 수 있다. 한담(寒痰)으로 오는 기침, 관절통, 식욕부진, 옹종(癰腫), 요통, 신경통, 류머티즘성관절염 등에 쓴다. 하루 3~6그램을 먹는다. 음허화왕(陰虛火旺)이나 열증(熱證)에는 쓰지 않는다. 짓찧어 찜질도 한다.]
해파리 냉채에 겨자를 넣어 먹고 눈물을 흘리지 않는 사람은 없다. 매운맛이 톡 쏘면서 입맛을 돋구는 뛰어난 천연 향신료이다. 중국의 <일용본초>에서는 개자에 관해서 기록하기를 "갈아서 가루내고 물에 개어서 정수리에 바르면 코피를 멎게하는 효능이 있다."라고 말한다. 관절염의 치료에는 개자가루 37그램, 식초 적당량을 쓴다. 먼저 개자가루를 소량의 끓인 물로 적시고 다시 식초를 넣고 풀처럼 개어서 천위에 펴고 가제를 위에 놓고 아픈 곳에 바른다. 3시간 후에 떼고 3~5일에 한 번씩 바르면 된다. <천금방>에서는 "이농의 치료에는 개자를 짓찧어 사람의 젖과 섞고 솜으로 그것을 싸서 귀안에 넣는다."라고 적고 있다. <손천인집효방>에서는 "눈썹이 나지 않을 때는 개자, 반하 각 같은 양을 가루내고 생강의 천연즙에 개어서 바른다."라고 기록한다.
갓의 씨앗인 종자의 효능도 대단하다. 온중산한, 이기활담, 통경락, 소종독 하는 효능이 있으며, 위한토식, 심복동통, 폐한해수, 통비, 급성 인후염 따위로 목이 부어 음식을 삼킬 때 심한 통증이 있는 증상, 처음엔 통증이 없다가 나중에 심하게 부어오르는 악성 종기, 유담, 타박상을 치료한다.
겨자의 성분에 대해서 일본에서 펴낸 <야채도감>에서는 이렇게 적고 있다.
[식품성분표(겨자채가식부 100g당, 생)
열량: 19kcal(79j)
수분: 92.5g
단백질: 2.9g
지질: 0.1g
탄수화물
당질: 2g
섬유질: 1.2g
회분: 1.3g
무기질
칼슘: 110mg
인: 55mg
철: 1.7mg
나트륨: 46mg
칼륨: 470mg
비타민
A레티놀: 0㎍
카로틴: 2,300㎍
A효력: 1,300㎍
B1: 0.09mg
B2: 0.21mg
나이아신: 0.9mg
C: 70mg
식염상당량: 0.1g]
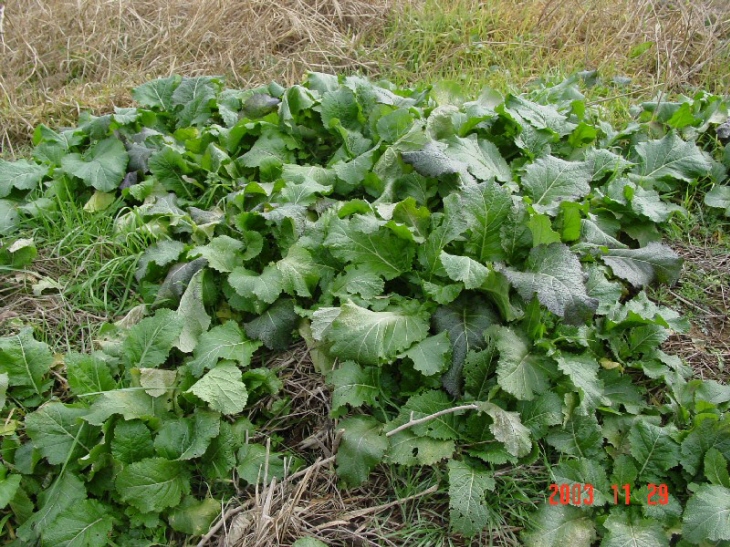
우리나라에서는 여수의 돌산 갓 김치를 떠올려 볼 수 있다. 돌산 갓의 특징은 해풍이 조화된 독특한 기후와 토양에서 자란 돌산갓은 모양이 크고 조직이 부드러우며 행신 효과가 탁월하다고 하며, 돌산갓 김치는 숙성과정이 최고에 달했을때 비타민 햠유량이 가장 높이 나타나며, 비타민B1, B2는 동물성 식품에만 존재하는 물질이지만, 돌산갓 김치에는 예외로 존재하며, 김이나 청각을 부재료로 사용하면 비타민 B1, B2가 더욱 많아진다고 한다. 젓갈을 넣을 경우 칼슘을 공급하고 각종 아미노산의 공급원이 되며 젓산발효로 부패균의 번식을 막고 발암성 물질의 발생을 억제한다고 한다.
우리나라 남부 지방에서는 겨울에도 들판이나 개울가에 얼어 죽지 않고 싱싱하게 자라는 갓을 흔히 볼 수 있다. 생김새가 마치 곰보배추를 닮았으나 곰보배추는 크기가 작고 향이 다르며 갓은 곰보배추보다 훨씬 크고 억세며 색깔이 다양하기 때문에 쉽게 구별이 된다. 아무데나 흔하게 자라는 갓을 잘 이용만 한다면 건강에 커다란 유익을 줄 것임을 믿어 의심치 않는다.


Mustard greens

Spunky and soulful describe the taste of mustard greens that add a pungent, peppery flavor to recipes in which they are featured. Although they are available throughout the year, they are in season from December through April when they are at their best and most readily available.
Mustard greens are the leaves of the mustard plant, Brassica juncea. The leaves of mustard greens can have either a crumpled or flat texture and may have either toothed, scalloped, frilled or lacey edges. In addition to providing wonderfully nutritious greens, this plant also produces the acrid-tasting brown seeds that are used to make Dijon mustard.
This chart graphically details the %DV that a serving of Mustard greens provides for each of the nutrients of which it is a good, very good, or excellent source according to our Food Rating System. Additional information about the amount of these nutrients provided by Mustard greens can be found in the Food Rating System Chart. A link that takes you to the In-Depth Nutritional Profile for Mustard greens, featuring information over 80 nutrients, can be found under the Food Rating System Chart.
- Health Benefits
- Description
- History
- How to Select and Store
- How to Enjoy
- Individual Concerns
- Nutritional Profile
- References
Mustard greens are jampacked with nutrients. They provide good to excellent amounts of 9 vitamins, 7 minerals, dietary fiber and protein. And if that were not impressive enough, being a member of the Brassica family along with broccoli, cabbage and Brussels sprouts, they also feature the health-promoting phytonutrients known as glucosinolates.
Free-Radical Scavenging Power
One of the unique features of mustard greens is that they are an excellent source of three notable antioxidants: vitamin E, vitamin C and vitamin A (through their concentration of beta-carotene). These three nutrients team up to scavenge free radicals, which are excessively interactive molecules that not only cause damage to the molecules with which they interact, but have been linked to a host of different diseases and health conditions. Beta-carotene and vitamin E exert their protective actions against free radicals in the lipid-soluble areas of the body, while vitamin C balances out the job by working in the body's water-soluble environment. By providing antioxidant protection in both the water and fat-soluble areas of the body, mustard greens may offer great benefit to individuals with conditions ranging from asthma to heart disease to menopausal symptoms ...just to name a few.
Breathe Easier with Mustard Greens
Vitamin C works to neutralize the free radicals that are responsible for causing smooth muscle contraction and airway constriction in asthma. Additionally, it assists with the breakdown of histamine, one of the inflammatory chemicals that is overproduced in asthma and many other immune-related disorders.
Vitamin E and beta-carotene compliment vitamin C by working to scavenge free radicals that lurk in fat-soluble environments. People who get more vitamin E have a lower risk of developing asthma, while increasing vitamin E intake has also been shown to improve lung function significantly. With regard to beta-carotene, people who eat a diet low in this important nutrient (or vitamin A, the vitamin that can be made from it) tend to be at a greater risk for asthma.
But that's not all when it comes to the benefits mustard greens can offer to help individuals with asthma. Mustard greens are also a very good source of magnesium, a mineral that helps smooth muscle cells, like those lining the bronchial tubes and lungs, to stay relaxed rather than constricting themselves and the airways of which they are a significant part. Adding mustard greens to their diets is one way that many persons with asthma can help improve their health since studies show that magnesium levels are low in many individuals with asthma.
Promote Lung Health
Another reason you'll breathe easier when mustard greens are part of your healthy way of eating? They're an excellent source of pro-vitamin A. If you or someone you love is a smoker, or if you are frequently exposed to secondhand smoke, then making vitamin A-rich foods, such as mustard greens, part of your healthy way of eating may save your life, suggests research conducted at Kansas State University.
While studying the relationship between vitamin A, lung inflammation, and emphysema, Richard Baybutt, associate professor of nutrition at Kansas State, made a surprising discovery: a common carcinogen in cigarette smoke, benzo(a)pyrene, induces vitamin A deficiency.
Baybutt's earlier research had shown that laboratory animals fed a vitamin A-deficient diet developed emphysema. His latest animal studies indicate that not only does the benzo(a)pyrene in cigarette smoke cause vitamin A deficiency, but that a diet rich in vitamin A can help counter this effect, thus greatly reducing emphysema.
Baybutt believes vitamin A's protective effects may help explain why some smokers do not develop emphysema. "There are a lot of people who live to be 90 years old and are smokers," he said. "Why? Probably because of their diet…The implications are that those who start smoking at an early age are more likely to become vitamin A deficient and develop complications associated with cancer and emphysema. And if they have a poor diet, forget it." If you or someone you love smokes, or if your work necessitates exposure to second hand smoke, protect yourself by making sure that at least one of the World's Healthiest Foods that are rich in vitamin A, such as mustard greens, is a daily part of your healthy way of eating.
Take Mustard Greens to Heart
Mustard greens contain numerous nutrients that can contribute to a healthy cardiovascular system, including the antioxidants, vitamin E, beta-carotene and vitamin C.
The vitamin E supplied by mustard greens is instrumental to a host of different mechanisms that reduce the development of atherosclerosis, including protecting LDL ("bad") cholesterol particles from oxidation and decreasing platelet clumping. Dietary intake of vitamin E and vitamin C is thought to be associated with a compound called paraoxonase, an enzyme that inhibits LDL and HDL oxidation. Beta-carotene, like vitamin C, is also able to increase vessel dilation and reduce vessel spasm. One study has shown that patients with the lowest level of beta-carotene intake had almost twice the risk of having a myocardial infarction (heart attack) compared to those with the highest intake. Low levels of vitamin C have also been associated with higher levels of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol and lower levels of HDL ("good")cholesterol.
In addition, mustard greens also feature concentrated amounts of other nutrients that can keep your heart healthy. Included among them are vitamin B6, folic acid and magnesium.
Mustard greens are a very good source of vitamin B6, which has been shown in studies to decrease platelet clumping and thereby decrease risk of thrombosis (clot formation). Blood vitamin B6 levels tend to be lower in coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction patients, and some believe that low blood vitamin B6 levels may actually be useful as an indicator of risk for myocardial infarction.
One reason for this belief is that vitamin B6 along with folic acid, another nutrient of which mustard greens are an excellent source, is instrumental for preventing the buildup of homocysteine, which contributes to atherosclerosis through its ability to damage the blood vessels, keeping them in a constant state of injury. In fact, folic acid is so important for cardiovascular function that a major 1995 study concluded that consumption of 400 micrograms per day of folic acid could prevent 28,000 cardiovascular deaths per year in the United States.
Magnesium is necessary for normal blood vessel tone and function. Since mustard greens are also a very good source of magnesium, they may be able to help lower high blood pressure and may even decrease the risk of heart attack.
Supporting Women's Health
Mustard greens may also be good for women going through menopause. They provide nutrients that are supportive of bone health. They are an excellent source of calcium, a higher intake of which can help to prevent bone loss that usually occurs at this stage of life. Women with osteoporosis also have low bone magnesium content and other signs of magnesium deficiency, so mustard greens would once again be helpful since they also provide concentrated amounts of this mineral. In addition, as noted above, the vitamin B6 and folic acid in mustard greens help to reduce the buildup of homocysteine. This plays an important role in promoting bone health, since homocysteine can obstruct collagen cross-linking, resulting in poor bone matrix and osteoporosis. One study showed that even postmenopausal women who were not considered deficient in folic acid lowered their homocysteine levels simply by supplementing with folic acid by itself.
In addition to bone health, the nutrients in mustard greens can help women who are going through this life passage in other ways. Magnesium has also been shown to be helpful in reducing stress and promoting normal sleeping patterns. Vitamin E, which was also mentioned earlier as an antioxidant found in mustard greens, has also been shown to decrease the occurrence of hot flashes that many women experience around menopause.
Phytonutrient Power for Optimal Health
Mustard greens are members of the Brassica family of vegetables, whose other members include vegetable superstars such as broccoli, cabbage and Brussels sprouts. Over the years, these vegetables have received a great deal of attention for their unique health-promoting properties. In addition to the extensive palette of vitamins and minerals they provide, mustard greens, as well as the other Brassica vegetables, also contain phytonutrients known as glucosinolates, members of the organosulfur chemical family. In plants, glucosinolates react with an enzyme called myrosinase that converts them into related active compounds known as indoles and isothiocyanates. Indoles and isothiocyanates appear to reduce the potential of carcinogens through their ability to beneficially modulate liver detoxification enzymes. They inhibit certain enzymes that normally activate carcinogens and also induce other enzymes that help to dismantle active carcinogens. These are the primary mechanisms through which these derivatives of compounds found in mustard greens are thought to contribute to preventing cancer.
Sulforaphane, a compound formed when cruciferous vegetables such as mustard greens are chopped or chewed, is already known to trigger the liver to produce enzymes that detoxify cancer-causing chemicals, inhibit chemically-induced breast cancers in animal studies, and induce colon cancer cells to commit suicide. Now a laboratory study published in the Journal of Nutrition shows sulforaphane also helps stop the proliferation of breast cancer cells, even in the later stages of their growth.
Protection against Rheumatoid Arthritis
While one study suggests that high doses of supplemental vitamin C makes osteoarthritis, a type of degenerative arthritis that occurs with aging, worse in laboratory animals, another indicates that vitamin C-rich foods, such as mustard greens, provide humans with protection against inflammatory polyarthritis, a form of rheumatoid arthritis involving two or more joints.
The findings, presented in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases were drawn from a study of more than 20,000 subjects who kept diet diaries and were arthritis-free when the study began, and focused on subjects who developed inflammatory polyarthritis and similar subjects who remained arthritis-free during the follow-up period. Subjects who consumed the lowest amounts of vitamin C-rich foods were more than three times more likely to develop arthritis than those who consumed the highest amounts.
Vitamin E-rich Leafy Greens Slow Loss of Mental Function
Mental performance normally declines with age, but the results of Chicago Health and Aging Project (CHAP) suggest that eating just 3 servings of green leafy, yellow and cruciferous vegetables each day could slow this decline by 40%, suggests a study in the journal Neurology (.Morris MC, Evans DA, et al.) Compared to people who consumed less than one serving of vegetables a day, people who ate at least 2.8 servings of vegetables a day saw their rate of cognitive decline slow by roughly 40%. This decrease is equivalent to about five years of younger age,
said lead author Martha Clare Morris, ScD, with Rush University Medical Center in Chicago.
The prospective cohort study, funded by the National Institute of Aging, used dietary data from 3,718 participants (62% female, 60% African American, average age 74). Mental function was assessed with four different tests: the East Boston Tests of immediate memory and delayed recall, the Mini-Mental State Examination, and the Symbol Digit Modalities Test, taken at the start of the study and then again after 3 and 6 years.
After adjusting the results for potential confounders such as age, sex, race, education, and cardiovascular risk factors, the researchers found that consuming an average of 2.8 vegetable servings each day was associated with a 40% decrease in cognitive decline, compared to those who ate an average of less than one (0.9) serving a day. Of the different types of vegetables, green leafy vegetables had the strongest association,
said Dr. Morris.
Surprisingly, no relationship was found between fruit consumption and cognitive decline.
Morris hypothesizes that this may be due to the fact that vegetables, but not fruits, contain high amounts of vitamin E, which helps lower the risk of cognitive decline. Also, vegetables, but not fruits, are typically consumed with a little fat, such as olive oil or salad dressing, which increases the body's ability to absorb vitamin E.
The Rush University researchers plan further research to understand why fruit appears to have little effect and to explore the effects of citrus fruit, specifically, on cognitive decline. Bottomline: If you remember to enjoy at least 3 servings of leafy greens each day, you are much more likely to remember other things as well!
Mustard greens are the leaves of the mustard plant, Brassica juncea. In addition to producing these wondrously nutritious greens, this plant also produces the acrid-tasting brown seeds that are used to make Dijon mustard.
Spunky and soulful describe the taste of mustard greens. Their pungent, peppery flavor adds a zing to any recipe in which they are featured.
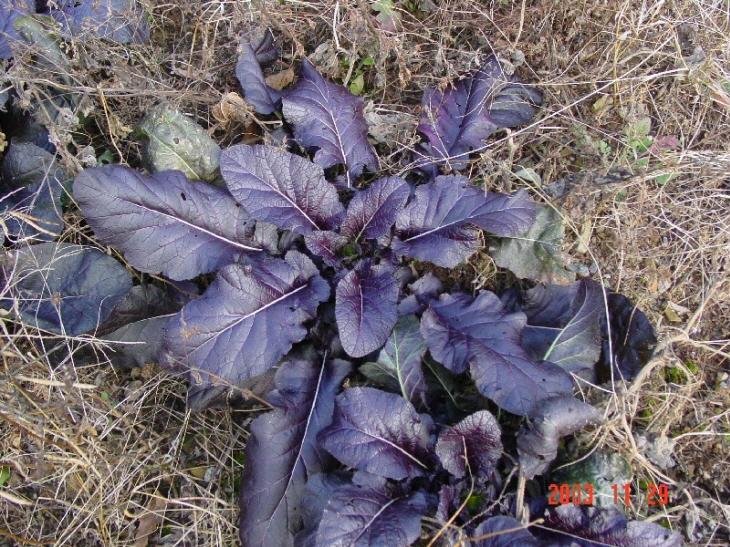
Mustard greens come in a host of varieties that each has distinct characteristics. Adding these brilliant leaves to your food preparations will certainly enhance the beauty of any meal. Most mustard greens are actually emerald green in color, while some are not green at all but rather shades of dark red or deep purple. The leaves of mustard greens can have either a crumpled or flat texture and may have either toothed, scalloped, frilled or lacey edges. Mizuna is one type of mustard green that is oftentimes available in stores.
Mustard greens originated in the Himalayan region of India and have been grown and consumed for more than 5,000 years. Mustard greens are a notable vegetable in many different cuisines, ranging from Chinese to Southern American. Like turnip greens, they may have become an integral part of Southern cuisine during the times of slavery, serving as a substitute for the greens that were an essential part of Western African foodways. While India, Nepal, China and Japan are among the leading producers of mustard greens, a significant amount of mustard greens are grown in the United States as well.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.